What is Alzheimer’s?
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive disease (fast-growing disease) of dementia. The word Dementia is used for conditions resulting from brain injuries or diseases that negatively affect memory, thinking, and behaviour.
According to the Alzheimer’s Association, Alzheimer’s disease is responsible for 60 to 80 percent of dementia cases. Most people with the disease are diagnosed after the age of 65. If it is diagnosed earlier, it is commonly referred to as early Alzheimer’s disease. There is no final cure for Alzheimer’s, but there are some treatments that can decrease the growth of the disease.
Alzheimer’s causes and risk factor
Experts haven’t determined a single cause of Alzheimer’s disease, but they have identified some risk factors, including age, family history, and Genetics.
Age: Most people who have Alzheimer’s disease are 65 years of age or older.
Family history: You are more likely to get it if you have a family member who has Alzheimer’s.
Genetics: Certain genes have been linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
These reasons do not mean that you will develop Alzheimer’s disease but it can increase your risk level.
You can talk to your doctor to find out more about the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease on you.
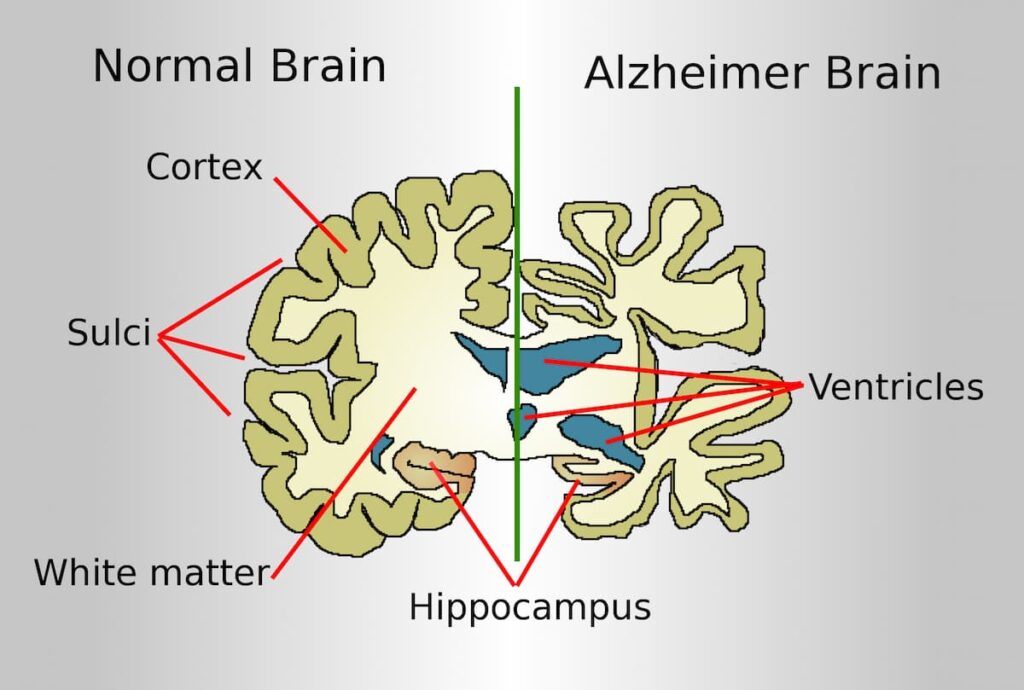
Alzheimer’s and Genetic Science
Although there is no recognizable cause for Alzheimer’s, genetics may play an important role. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) is a gene associated with the onset of Alzheimer’s symptoms in senior citizens. Blood tests can determine whether you have this gene, which increases your risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
But keep in mind that even if someone has this gene, they may not have Alzheimer’s. In contrast, some people may have Alzheimer’s even if they do not have this gene. There is no way to know for sure if someone has Alzheimer’s. Other genes may also increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s and Alzheimer’s.
Early symptoms of Alzheimer’s
Alzheimer’s usually affects people 65 years of age and older. However, it can also occur in people as early as the age of 40 or 50. This is called the early onset of Alzheimer’s. This type of Alzheimer’s affects up to 5 percent with this condition. Symptoms of early Alzheimer’s may be mild memory loss and feeling uncomfortable with everyday tasks.
Symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease:
By the way, the habit of forgetting appears in everyone from time to time. However, the behaviour and symptoms of people with Alzheimer’s disease change over time. Following are some of the major symptoms.
- Memory loss that is affecting your daily activities
- Facing difficulties in solving the problems
- Trouble with speech or writing
- Being confused about times or places
- Lack of decision-making
- Lack of personal hygiene
- Mood and personality changes
- Making distance from friends, family and society
Late-stage Alzheimer’s (severe)
In the final stage of the disease, dementia symptoms are severe.
They will lose the ability to respond. They will forget about the conversation, and may still say words or phrases, but telling pain becomes difficult. As memory and cognitive skills continue to worsen, significant personality changes may take place and individuals need extensive care.
At this stage,
They require around-the-clock assistance with daily personal care.
They will lose awareness of recent experiences as well as of their surroundings.
They will experience difficulty in physical abilities, including walking, sitting and, eventually, swallowing
They will have difficulty communicating with others.
They become vulnerable to infections, especially pneumonia.
Alzheimer’s preventing
Just as there is no known cure for Alzheimer’s, there is no proven cure. However, researchers say that this can be overcome by improving the lifestyle to prevent its symptoms.
The following things may help:
Doing Breathing Exercises 2 times daily (Pranayama)
- Avoid smoking
- Exercise regularly
- Participate in activities that involve brain exercises
- Eat green vegetables, fruits
- Consume more antioxidants
- Maintain an active social life
- Talk to the doctor before making any major changes to your lifestyle.
Alzheimer’s Dementia has no cure. But there is a way to reduce the risk or prevent it. First need a complete awareness of brain health and need to live healthy and eat healthy from a young age. if the symptoms arise at the age of 55-60, Alzheimer’s Dementia was already started 20 years before.
There are many things that can lead to Alzheimer’s Dementia. For example, Depression, Anxiety and stress will be the major cause of Alzheimer’s if not treated in time. There are other possible factors like unhealthy lifestyle, unhealthy food, no physical activity, too much alcohol, poor nutrition, bad working environment, family violence, loneliness, and too much eating of meat protein. What is good for your heart is also good for your brain.
Alzheimer in Nepali




